Unity是 实时3D互动内容创作和运营平台 。包括游戏开发、美术、建筑、汽车设计、影视在内的所有创作者,借助 Unity 将创意变成现实。Unity 平台提供一整套完善的软件解决方案,可用于创作、运营和变现任何实时互动的2D和3D内容,支持平台包括手机、平板电脑、PC、游戏主机、增强现实和虚拟现实设备。简单来说,Unity3D不单单可以做游戏,还可以通过相关接口与API来进行设备的交互【例如虚拟仿真】
【此文章所有代码可在文章末尾下载查看源码 】
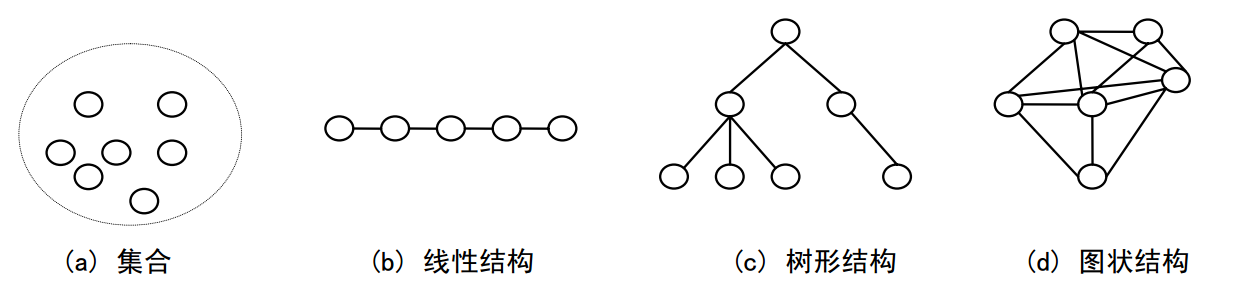
数据结构是计算机存储,组织数据的方式,同样也是相互之间存在一种或者多种特定关系的数据元素的集合
算法是一系列规定的计算步骤,为了实现特定的计算目的
基本数据结构一般有4类:
集合:数据结构中的集合与数学中的集合类似,在集合中的 数据只是存在同一集合中,但其数据之间没有关系 。
线性结构:数据元素之间是一对一的关系
主要包括:线性表,栈,队列(三者的数据元素以及数据间的逻辑关系完全相同,差别就在于线性表的操作不受限制,而栈和队列的操作受到限制,栈的操作只能在表的一端进行,队列的插入操作在表的一端进行而其它操作在表的另一端进行,所以,把栈和队列称为操作受限的线性表)
树形结构:数据元素之间的层次关系是一对多
图形结构:**数据元素之间呈多对多的关系
数组 静态数组: int[],float[],string[]等
特点:数组一旦创建,其容量的大小是无法进行改变的
动态数组: ArrayList List
特点:可以根据元素的多少动态的调整数组容量的大小
泛型数组(List): 优势:对于存储值类型数据,性能更优;使代买更清晰和保证类型安全
动态数组代码实现 这里主要考虑的便是数组中所要实现的功能(插入数据,获取数据,删除数据,修改数据,数组的扩容)
(1).定义一个数组来存储数据T[] data,通过num来统计数组的数组的大小
1 2 private T[] data;private int num;
(2).所需要的参数定义完毕后便是对构造方法,这里主要考虑的便是数组需要在创建之初要设置好数组的大小
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public ArrayOne (int capacity data = new T[capacity]; num = 0 ; } public ArrayOne (): this (10
(3).考虑使用过程中所需要的功能【添加数据,修改数据,删除数据,获取数据,扩容数组】
插入/添加数据 ①.首先需要判定index是否在数组范围内
1 if (index < 0 || index >num )throw new ArgumentException("index不合法,请检查" );
②.由于我们使用的是动态数组,当数组的长度和num相同时,则需要对数组进行扩容【相关代码请看ResetCapacity()方法】
1 2 if (num == data.Length) ResetCapacity(2 *data.Length);
③下面我们要考虑的便是添加数据,这里主要考虑的便是插入的目标索引和数据信息,需要将目标位置索引数据往后挪动,然后将目标索引的数据写入即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public void Add (int index,T e if (index < 0 || index >num )throw new ArgumentException("index不合法,请检查" ); if (num == data.Length) ResetCapacity(2 *data.Length); for (int i = num - 1 ; i >= index; i--) data[i+1 ]=data[i]; data[index] = e; num++; }
④这里为了方便添加了向数据末尾和数据头部添加数据的方法,只需将num和数据添加写入即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void AddLast (T value ) Add(num,value ); } public void AddFist (T value ) Add(0 ,value ); }
获取数据 这里考虑的比较少一些,只需判断所要获取的索引是否越界,然后返回相应索引的数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public T Get (int index if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); return data[index]; } public T GetFirst ()return Get(0 ); }public T GetLast ()return Get(num-1 ); }
修改数据 这里考虑的比较少一些,只需判断所要获取的索引是否越界,将相应索引的数据重新赋值即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public void SetValue (int index,T newValue{ if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); data[index] = newValue; }
删除数据 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 public T RemoveFirst ()return RemoveAt(0 ); }public T RemoveLast ()return RemoveAt(num-1 ); }public string Remove (int value int index=IndexOf(value ); if (index != -1 ) { RemoveAt(index); return "删除成功" ; } else return "所要删除的数据不存在,故删除失败" ; } public T RemoveAt (int index if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); T delValue=data[index]; for (int i = index+1 ; i <=num-1 ; i++) data[i-1 ] = data[i]; num--; data[num] = default (T); if (num == data.Length / 4 ) ResetCapacity(data.Length / 2 ); return delValue; }
判断数据存在 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public bool Contains (T value ){ for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { if (data[i].Equals(value )) return true ; } return false ; }
下面是完整代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 private T[] data; private int num; public ArrayOne (int capacity data = new T[capacity]; num = 0 ; } public ArrayOne (): this (10 public int Capacity { get { return data.Length; } } public int Count{ get { return num; } } public bool IsEmpty{ get { return num == 0 ; } } public T Get (int index if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); return data[index]; } public T GetFirst ()return Get(0 ); } public T GetLast ()return Get(num-1 ); } public void SetValue (int index,T newValue { if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); data[index] = newValue; } public override string ToString () StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.Append(string .Format("ArrayOne: count={0} capacity={1}\n" ,num,data.Length)); stringBuilder.Append("[" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { stringBuilder.Append(data[i]); if (i != num - 1 ) stringBuilder.Append(", " ); } stringBuilder.Append("]" ); return stringBuilder.ToString(); } public bool Contains (T value ) { for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { if (data[i].Equals(value )) return true ; } return false ; } public int IndexOf (int value for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) { if (data[i].Equals(value )) return i; } return -1 ; } public T RemoveAt (int index if (index < 0 || index >= num) throw new ArgumentException("数组索引越界" ); T delValue=data[index]; for (int i = index+1 ; i <=num-1 ; i++) data[i-1 ] = data[i]; num--; data[num] = default (T); if (num == data.Length / 4 ) ResetCapacity(data.Length / 2 ); return delValue; } public T RemoveFirst ()return RemoveAt(0 ); } public T RemoveLast ()return RemoveAt(num-1 ); } public string Remove (int value int index=IndexOf(value ); if (index != -1 ) { RemoveAt(index); return "删除成功" ; } else return "所要删除的数据不存在,故删除失败" ; } private void ResetCapacity (int newCapacity { T[] newData=new T[newCapacity]; for (int i = 0 ; i < num; i++) newData[i]=data[i]; data=newData; } }
具体测试代码详见
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 ArrayOne<int > arrayOne = new ArrayOne<int >(20 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { arrayOne.AddLast(i); } Console.WriteLine("数组信息:{0}" , arrayOne); arrayOne.AddLast(1234 ); Console.WriteLine("**********末尾添加完数据后的数组信息:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); arrayOne.AddFist(88 ); Console.WriteLine("**********头部添加完数据后的数组信息:**********\ns{0}" , arrayOne); Console.WriteLine("获取数组头部元素:{0}" , arrayOne.GetFirst()); Console.WriteLine("获取数组尾部元素:{0}" , arrayOne.GetLast()); Console.WriteLine("获取数组第6个元素:{0}" , arrayOne.Get(6 )); arrayOne.SetValue(2 , 755 ); Console.WriteLine("**********修改第2个数组元素后:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); bool isHave= arrayOne.Contains(78 );Console.WriteLine("arrayOne中{0}存在78" ,isHave?"" :"不" ); Console.WriteLine("返回数据3的相关索引:{0}" , arrayOne.IndexOf(3 )); arrayOne.RemoveAt(3 ); Console.WriteLine("**********删除索引为3的数据后:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); arrayOne.RemoveFirst(); Console.WriteLine("**********删除头索引的数据后:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); arrayOne.RemoveLast(); Console.WriteLine("**********删除末尾索引的数据后:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); string s=arrayOne.Remove(7777 );Console.WriteLine(s); Console.WriteLine("**********尝试删除7777的数据后数组:**********\n{0}" , arrayOne); Console.ReadLine();
控制台输出效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 数组信息:ArrayOne: count=10 capacity=20 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ] **********末尾添加完数据后的数组信息:********** ArrayOne: count=11 capacity=20 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1234 ] **********头部添加完数据后的数组信息:********** sArrayOne: count=12 capacity=20 [88, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1234 ] 获取数组头部元素:88 获取数组尾部元素:1234 获取数组第6 个元素:5 **********修改第2 个数组元素后:********** ArrayOne: count=12 capacity=20 [88, 0, 755, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1234 ] arrayOne中不存在78 返回数据3 的相关索引:4 **********删除索引为3 的数据后:********** ArrayOne: count=11 capacity=20 [88, 0, 755, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1234 ] **********删除头索引的数据后:********** ArrayOne: count=10 capacity=20 [0, 755, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 1234 ] **********删除末尾索引的数据后:********** ArrayOne: count=9 capacity=20 [0, 755, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ] 所要删除的数据不存在,故删除失败 **********尝试删除7777 的数据后数组:********** ArrayOne: count=9 capacity=20 [0, 755, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]
线性表 List相关常用属性
1 2 *1.list.Add(T t)//T代表所存储的数据类型,将数据t存入链表末尾 *2.public void Insert(int index, T item);//插入数据,index代表下角标,item代表数据
1 2 3 1.public bool Contains(T item)//查找是否包含 item 2.public T Find(Predicate<T> match); 返回满足条件的第一个值 3.public int IndexOf(T item, int index, int count);//index开始下标,count查找个数,item查找对象
1 2 3 4 5 *1.public void Clear();//清除所有数据 *2.public int RemoveAll(Predicate<T> match);//删除满足条件 *3.public bool Remove(T item);//移处数据 *4.public void RemoveAt(int index);//移除下角标为index的值 5.public void RemoveRange(int index, int count);//从下角标为index的值开始count个数
线性表的存储结构
线性表的实现方式:
顺序表 定义:线性表的顺序存储是指在内存中用一块地址连续的空间依次存放线性表的数据元素,简单说把表中的元素一个接一个地放进顺序的存储单元
顺序表要求数据要按照顺序进行存储,同理在内存中也同样是按照顺序进行存储。
顺序表的优点:用地址连续的存储单元顺序存储线性表中的各个数据元素,逻辑上相邻的数据元素在物理位置上也相邻,所以查找任何一个位置上的数据元素非常方便 ;
顺序表的缺点:进行插入和删除时,需要通过移动数据元素来实现,影响了运行效率
顺序表代码实现
【1】IListDS接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public interface IListDS <T > { int GetLength () void Clear () bool IsEmpty () void Add (T item ) void Insert (T item, int i ) T Delete (int i ; T GetElem (int i ; T this [int index] { get ; } int Locate (T value ) }
【2】SeqList
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 class SeqList <T > : IListDS <T >{ public T[] data; private int count=0 ; public SeqList (int size { data = new T[size]; count = 0 ; } public SeqList () : this (10 public T this [int index] { get { return GetElem(index); } } public void Add (T item ) { if (count == data.Length){ Console.WriteLine("当前顺序表已经存满,不允许在存入数据" ); } else { data[count] = item; count++; } } public void Clear () count = 0 ; } public T Delete (int index T temp=data[index]; for (int i = index+1 ; i < count; i++) { data[i - 1 ] = data[i]; } count--; return temp; } public T GetElem (int index if (index >= 0 && index <= count - 1 ) { return data[index]; } else { Console.WriteLine("索引不存在" ); return default (T); } } public int GetLength () return count; } public void Insert (T item, int index ) for (int i = count-1 ; i>=index; i--) { data[i+1 ]=data[i]; } data[index] = item; count++; } public bool IsEmpty () return count == 0 ; } public int Locate (T value ) for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { if (data[i].Equals(value )) { return i; } } return -1 ; } }
具体测试代码详见
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 SeqList<string > seqList = new SeqList<string >(); seqList.Add("计算机学院" ); seqList.Add("软件学院" ); seqList.Add("艺术学院" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < seqList.GetLength(); i++) { Console.WriteLine("数据{0}:{1}" , i, seqList[i]); } Console.WriteLine("顺序表长度:" +seqList.GetLength()); Console.WriteLine("顺序表中第一个数值:" + seqList.GetElem(0 )); Console.WriteLine("删除顺序表中第二个数据:" +seqList.Delete(2 )); Console.WriteLine("顺序表长度:" + seqList.GetLength()); seqList.Insert("工程学院" , 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < seqList.GetLength(); i++) { Console.WriteLine("添加完后的数据{0}个:{1}" , i, seqList[i]); } Console.WriteLine("顺序表长度:" + seqList.GetLength()); Console.WriteLine("数据所在位置:" +seqList.Locate("艺术学院" )+"【注:-1代表未查询到】" );
控制台输出效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 数据0:计算机学院 数据1:软件学院 数据2:艺术学院 顺序表长度:3 顺序表中第一个数值:计算机学院 删除顺序表中第二个数据:艺术学院 顺序表长度:2 添加完后的数据0个:计算机学院 添加完后的数据1个:工程学院 添加完后的数据2个:软件学院 顺序表长度:3 数据所在位置:-1【注:-1代表未查询到】
链表 优点:
一般数组都是需要一连串的内存空间来存储数据,但是链表结构不需要一连串的内存空间。此外,由于它具有的独特的结构,使得链表插入数据变得非常的快捷。因为它不需要移动后面的数据。List列表中间插入一个数据时,后面所有的数据都要进行移动。
缺点:
链表每个节点都是离散的,所以访问链表中数据只能一个接着一个访问,这需要较长的时间来查找位于链表中间或尾部的元素。访问数据效率就会变得低下。
单链表 定义:如果结点的引用域只存储该结点直接后继结点的存储地址,则该链表叫单链表
单向链表的每一个节点又包含两部分,一部分是存放数据的变量 data(值) ,另一部分是指向下一个节点的 next(下个位域)指针
单链表结点的结构如图所示
data 表示结点的数据域
next代表该引用域,即指向另一个结点
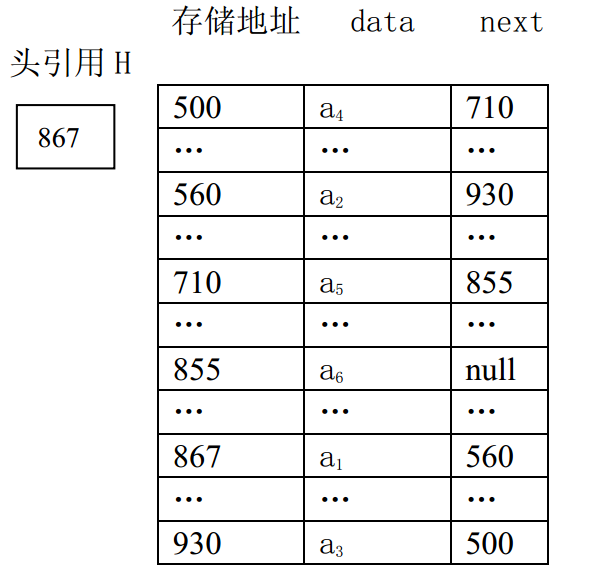
下图是线性表(a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6)对应的链式存储结构示意图
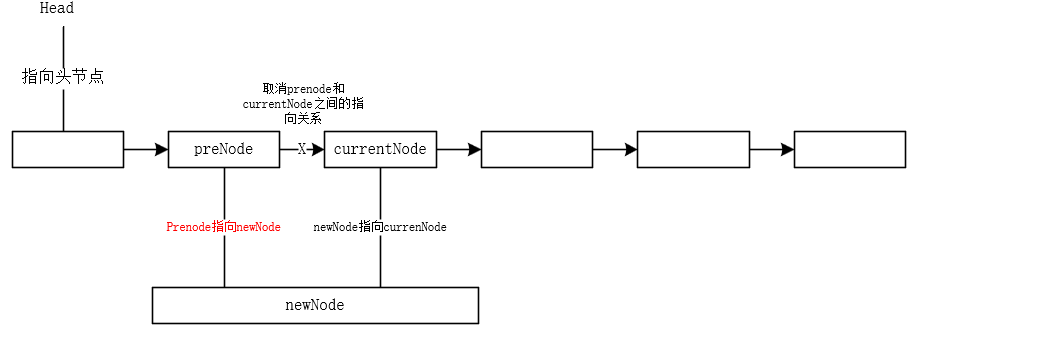
需要考虑插入的位置:(1)若插入的位置在头部为空时,只需将节点的next为head即可 (2)如果插入到其他部分(假设插入位置为n),则需将n-1和n位置next连接切断,将n-1的next指向新的n,新的n的next指向原本的n,即可完成单链表插入数据操作。
添加数据比插入数据较为简单,但是也需要判断head结点是否为空,如果为空的话,将新添加的结点设置为head即可,若head结点不是空的,则需要通过遍历结点,判断结点的next是否为空,如next为空,则将新的结点放到链表尾部,即可完成添加操作。
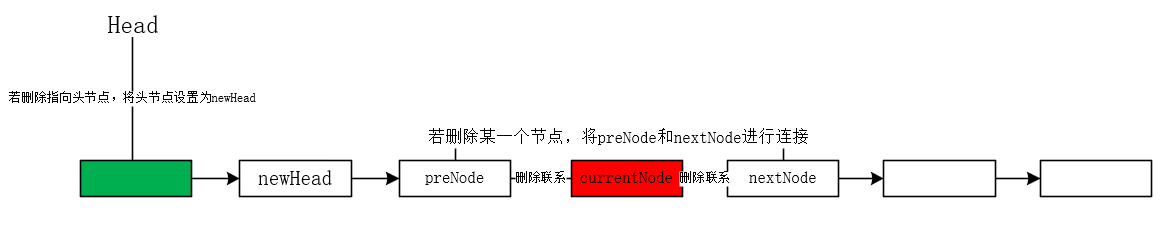
移除某个数据时,需要判断删除的位置,若删除的位置在于head,则需将head结点指向新的newNode,若删除的位置在于n个位置,则需通过for循环到所删除位置的n-1位置,将其定义为preNode,将n定义为currentNode,由于需要删除currentNode,所以要获取currentNode的next结点,也就是nextNode,将preNode的next更改为nextNode即可完成删除数据操作【这里无需考虑删除位置为末尾所导致的没有next,因为在Node构造方法中next可以】
单链表代码实现
【1】IListDS接口==>用于设定单链表所要实现的相关方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public interface IListDS <T >{ int GetLength () void Clear () bool IsEmpty () void Add (T item ) void Insert (T item, int i ) T Delete (int i ; T GetElem (int i ; T this [int index] { get ; } int Locate (T value ) }
【2】Node
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Node <T >{ private T data; private Node<T> next; public T Data { get => data; set => data = value ; } internal Node<T> Next { get => next; set => next = value ; } public Node () data=default (T); next=null ; } public Node (T value ) data=value ; next=null ; } public Node (Node<T> next ) this .next = next; } public Node (T data, Node<T> next ) this .data = data; this .next = next; } }
【3】LinkList
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 class LinkList <T > : IListDS <T > { private Node<T> head; public LinkList () { head = null ; } public T this [int index] { get { Node<T> temp = head; for (int i = 1 ; i <= index; i++){ temp = temp.Next; } return temp.Data; } } public void Add (T item ) Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item); if (head==null ) head = newNode; else { Node<T> temp = head; while (true ) { if (temp.Next != null ) { temp=temp.Next; } else { break ; } } temp.Next = newNode; } } public void Clear () head=null ; } public T Delete (int index T data = default (T); if (index==0 ){ data =head.Data; head=head.Next; } else { Node<T> temp = head; for (int i = 1 ; i <= index - 1 ; i++){ temp = temp.Next; } Node<T> preNode = temp; Node<T> currentNode = temp.Next; data = currentNode.Data; Node<T> nextNode = temp.Next.Next; preNode.Next = nextNode; } return data; } public T GetElem (int index return this [index]; } public int GetLength () if (head == null ) return 0 ; Node<T> temp = head; int count = 1 ; while (true ){ if (temp.Next != null ){ count++; temp = temp.Next; } else { break ; } } return count; } public void Insert (T item, int index ) Node<T> newNode=new Node<T>(item); if (index == 0 ) { newNode.Next = head; head = newNode; } else { Node<T> temp = head; for (int i = 1 ;i<=index-1 ;i++){ temp=temp.Next; } Node<T> preNode = temp; Node<T> currentNode = temp.Next; preNode.Next = newNode; newNode.Next = currentNode; } } public bool IsEmpty () return head == null ; } public int Locate (T value ) Node<T> temp=head; if (temp == null ) return -1 ; else { int index = 0 ; while (true ) { if (temp.Data.Equals(value )){ return index; } else { if (temp.Next != null ) { temp = temp.Next; index++; } else { break ; } } } return -1 ; } } }
具体测试代码详见
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 nodeList.Add("计算机科学与技术" ); nodeList.Add("软件工程" ); nodeList.Add("自动化" ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nodeList.GetLength(); i++) { Console.WriteLine("数据{0}:{1}" , i, nodeList[i]); } Console.WriteLine("单链表长度:" + nodeList.GetLength()); Console.WriteLine("单链表中第一个数值:" + nodeList.GetElem(0 )); Console.WriteLine("删除单链表中第二个数据:" + nodeList.Delete(2 )); Console.WriteLine("单链表长度:" + nodeList.GetLength()); nodeList.Insert("艺术与实践" , 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nodeList.GetLength(); i++) { Console.WriteLine("添加完后的数据{0}个:{1}" , i, nodeList[i]); } Console.WriteLine("单链表长度:" + nodeList.GetLength()); Console.WriteLine("数据所在位置:" + nodeList.Locate("软件工程" ) + "【注:-1代表未查询到】" );
控制台输出效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 数据0:计算机科学与技术 数据1:软件工程 数据2:自动化 单链表长度:3 单链表中第一个数值:计算机科学与技术 删除单链表中第二个数据:自动化 单链表长度:2 添加完后的数据0个:计算机科学与技术 添加完后的数据1个:艺术与实践 添加完后的数据2个:软件工程 单链表长度:3 数据所在位置:2【注:-1代表未查询到】
双链表 含义:
双向链表其元素指向它前面和后面的元素。它的每一个节点除了拥有 data 和 next 指针,还拥有指向前置节点的 prev (上个位域)指针
特性:
1)LinkedList 无法通过下标查找元素 ,在查找链表元素时,总是从头结点开始查找。
2)LinkedList 的容量是链表最大包含的元素数,会根据元素增减而动态调整容量 。
3)LinkedList 中的每个节点 都属于 LinkedListNode 类型 。
4)LinkedList 的值可以为 null,并允许重复值 。
5)LinkedList **不自带排序方法。
栈和队列 栈 原则:(后进先出/先进后出)
定义:
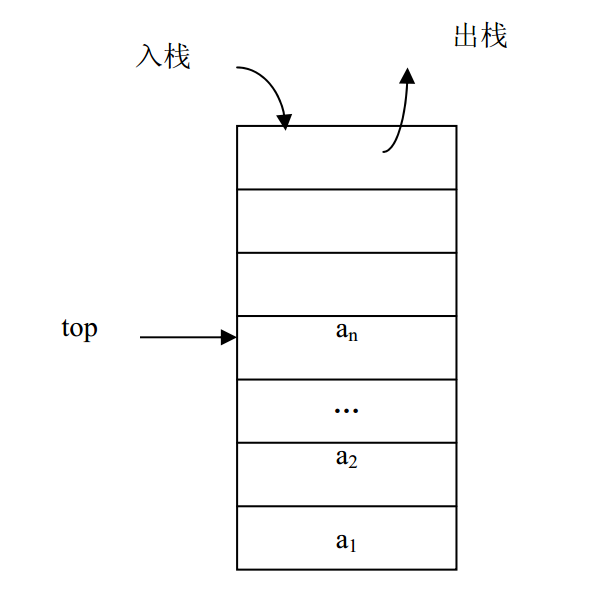
栈是操作限定在表的尾端进行的线性表。表尾由于要进行插入、删除等操作,所以,它具有特殊的含义,把表尾称为栈顶( Top),另一端是固定的,叫栈底( Bottom)。当栈中没有数据元素时叫空栈(Empty Stack)
删除栈元素的方式是:例如a1,需要将a1以上的 元素先移除出去,才能移除a1
使用BCL
在BCL(基本类库)中提供了泛型的Stack类【C#2.0开始】
主要方法如下
1.Push()入栈(添加数据)
2.Pop()出栈(删除栈顶数据,返回被删除的数据 )
3.Peek()取栈顶数据(取得栈顶的数据,不删除 )
4.Clear()清空所有数据
5.count取得栈中数据的个数
栈的基本使用【代码】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Stack<string > stack = new Stack<string >(); stack.Push("abc" ); stack.Push("def" ); stack.Push("ghi" ); Console.WriteLine("栈的大小:" +stack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string temp= stack.Pop();Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈顶数据是:" +temp); Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈中的数据个数:" +stack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string tempTwo = stack.Peek();Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈顶数据是:" + tempTwo); Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈中的数据个数:" + stack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); Console.WriteLine("判断栈是否存在相关数据:" + stack.Contains("abc" )); stack.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("Clear后的栈中的数据个数:" + stack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); Console.WriteLine("判断栈是否存在相关数据:" +stack.Contains("abc" )); Console.ReadLine();
控制台输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 栈的大小:3 -------------------------------------------- Pop后的栈顶数据是:ghi Pop后的栈中的数据个数:2 -------------------------------------------- Peek后的栈顶数据是:def Peek后的栈中的数据个数:2 -------------------------------------------- 判断栈是否存在相关数据:True Clear后的栈中的数据个数:0 -------------------------------------------- 判断栈是否存在相关数据:False
代码实现
创建接口 IStackDS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public interface IStackDS <T > { int Count { get ; } int GetLength () bool isEmpty () void Clear () void Push (T item ) T Pop () ; T Peek () ; }
顺序栈 【第一种存储方式】(用一片连续的存储空间来存储栈中的数据元素(使用数组))
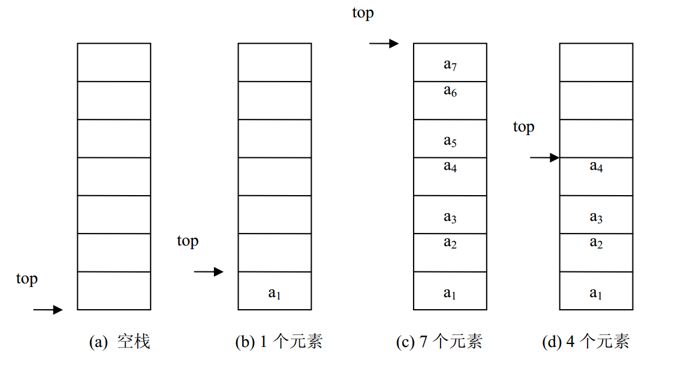
用一维数组来存放顺序栈中的数据元素。栈顶指示器 top 设在数组下标为 0 的端, top 随着插入和删除而变化,当栈为空时,top=-1。下图是顺序栈的栈顶指示器 top 与栈中数据元素的关系图。
创建 SeqStack
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class SeqStack <T > : IStackDS <T > { private T[] data; private int top; public SeqStack (int size data = new T[size]; top = -1 ; } public SeqStack () : this (15 } public int Count { get { return top + 1 ; } } public void Clear () top = -1 ; } public int GetLength () return Count; } public bool isEmpty () return Count == 0 ; } public T Peek () return data[top]; } public T Pop () T temp=data[top]; top--; return temp; } public void Push (T item ) data[top+1 ] = item; top++; } }
测试相关方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Console.WriteLine("使用自定义顺序栈" ); IStackDS<string > newstack = new SeqStack<string >(); newstack.Push("123" ); newstack.Push("456" ); newstack.Push("789" ); Console.WriteLine("栈的大小:" + newstack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string newtemp = newstack.Pop(); Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈顶数据是:" + newtemp); Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈中的数据个数:" + newstack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string newtempTwo = newstack.Peek(); Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈顶数据是:" + newtempTwo); Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈中的数据个数:" + newstack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); stack.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("Clear后的栈中的数据个数:" + newstack.Count); Console.ReadLine();
控制台输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 使用自定义顺序栈 栈的大小:3 -------------------------------------------- Pop后的栈顶数据是:789 Pop后的栈中的数据个数:2 -------------------------------------------- Peek后的栈顶数据是:456 Peek后的栈中的数据个数:2 -------------------------------------------- Clear后的栈中的数据个数:2
链栈 【第二种实现方式】(用单链表来表示,它的实现是单链表的简化,链栈结点的结构与单链表结点的结构一样)
注意:链栈的操作只是在一端进行,为了操作方便,把栈顶设在链表的头部,并且不需要头结点
把链栈看作一个泛型类,类中有一个字段 top 表示栈顶指示器。由于栈只能访问栈顶的数据元素,而链栈的栈顶指示器又不能指示栈的数据元素的个数。所以,求链栈的长度时,必须把栈中的数据元素一个个出栈,每出栈一个数据元素,计数器就增加 1,但这样会破坏栈的结构。为保留栈中的数据元素,需把出栈的数据元素先压入另外一个栈,计算完长度后,再把数据元素压入原来的栈。但这种算法的空间复杂度和时间复杂度都很高,所以,以上两种算法都不是理想的解决方法。理想的解决方法是 LinkStack类增设一个字段 num 表示链栈中结点的个数。
创建链栈结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Node <T > { private T data; private Node<T> next; public Node () Data=default (T); Next=null ; } public Node (T data ) this .Data = data; Next = null ; } public Node (Node<T> next ) this .Next=next; this .Data=default (T); } public Node (T data, Node<T> next ) this .Data=data; this .Next = next; } public T Data { get => data; set => data = value ; } internal Node<T> Next { get => next; set => next = value ; } }
创建链栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public class LinkStack <T > : IStackDS <T > { private Node<T> top; private int count; public int Count { get { return count; } } public int GetLength () return count; } public void Clear () count = 0 ; top= null ; } public bool isEmpty () return count == 0 ; } public T Peek () return top.Data; } public T Pop () T data = top.Data; top = top.Next; return data; } public void Push (T item ) Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item); newNode.Next = top; top = newNode; count++; } }
测试相关方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Console.WriteLine("使用代码实现链栈" ); IStackDS<string > newLinkStack=new LinkStack<string >(); newLinkStack.Push("西游记" ); newLinkStack.Push("三国演义" ); newLinkStack.Push("红楼梦" ); newLinkStack.Push("水浒传" ); Console.WriteLine("栈的大小:" + newLinkStack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string newLinktemp = newLinkStack.Pop(); Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈顶数据是:" + newLinktemp); Console.WriteLine("Pop后的栈中的数据个数:" + newLinkStack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); string newLinktempTwo = newLinkStack.Peek(); Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈顶数据是:" + newLinktempTwo); Console.WriteLine("Peek后的栈中的数据个数:" + newLinkStack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" ); newLinkStack.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("Clear后的栈中的数据个数:" + newLinkStack.Count); Console.WriteLine("--------------------------------------------" );
控制台输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 使用代码实现链栈 栈的大小:4 -------------------------------------------- Pop后的栈顶数据是:水浒传 Pop后的栈中的数据个数:4 -------------------------------------------- Peek后的栈顶数据是:红楼梦 Peek后的栈中的数据个数:4 -------------------------------------------- Clear后的栈中的数据个数:0 --------------------------------------------
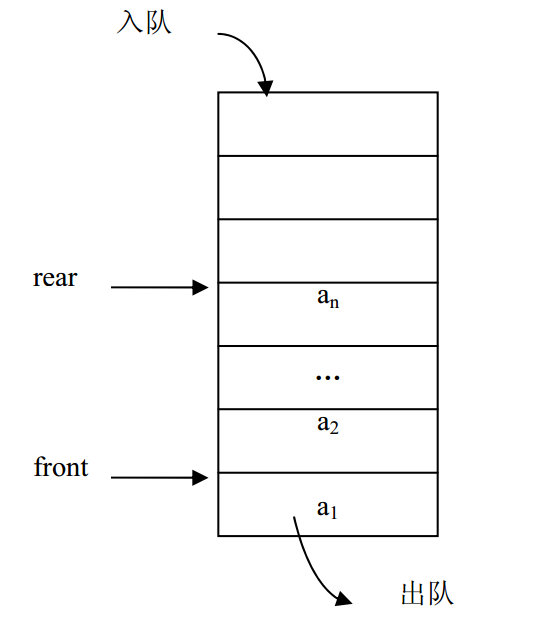
队列 原则:(先进先出,后进后出)
定义
队列(Queue)是插入操作限定在表的尾部而其它操作限定在表的头部进行的线性表。把进行插入操作的表尾称为队尾(Rear),把进行其它操作的头部称为队头(Front)。当队列中没有数据元素时称为空队列(Empty Queue)。
使用BCL
主要方法
1,Enqueue()入队(放在队尾)
主要属性
1,Count获取队列中元素的个数
使用BCL的队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Console.WriteLine("************使用BCL的队列************" ); Queue<string > queue = new Queue<string >(); queue.Enqueue("王者荣耀" ); queue.Enqueue("和平精英" ); queue.Enqueue("使命召唤M" ); Console.WriteLine("加入完三个游戏名称后的队列大小为:" +queue.Count); var tempOne=queue.Dequeue();Console.WriteLine("取得队首的数据为:" +tempOne); Console.WriteLine("出队之后的队列大小为:" +queue.Count); var tempTwo = queue.Peek();Console.WriteLine("取得队首的数据为:" + tempTwo); Console.WriteLine("Peek之后的队列大小为:" + queue.Count); queue.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("Clear之后的队列大小为:" +queue.Count); Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------" );
控制台输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ************使用BCL的队列************ 加入完三个游戏名称后的队列大小为:3 取得队首的数据为:王者荣耀 出队之后的队列大小为:2 取得队首的数据为:和平精英 Peek之后的队列大小为:2 Clear之后的队列大小为:0 ---------------------------------------
代码实现
定义IQueue接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public interface IQueue <T > { int Count{get ;} int GetLength () bool IsEmpty () void Clear () void Enqueue (T item ) T Dequque () ; T Peek () ; }
顺序队列 (用一片连续的存储空间来存储队列中的数据元素)
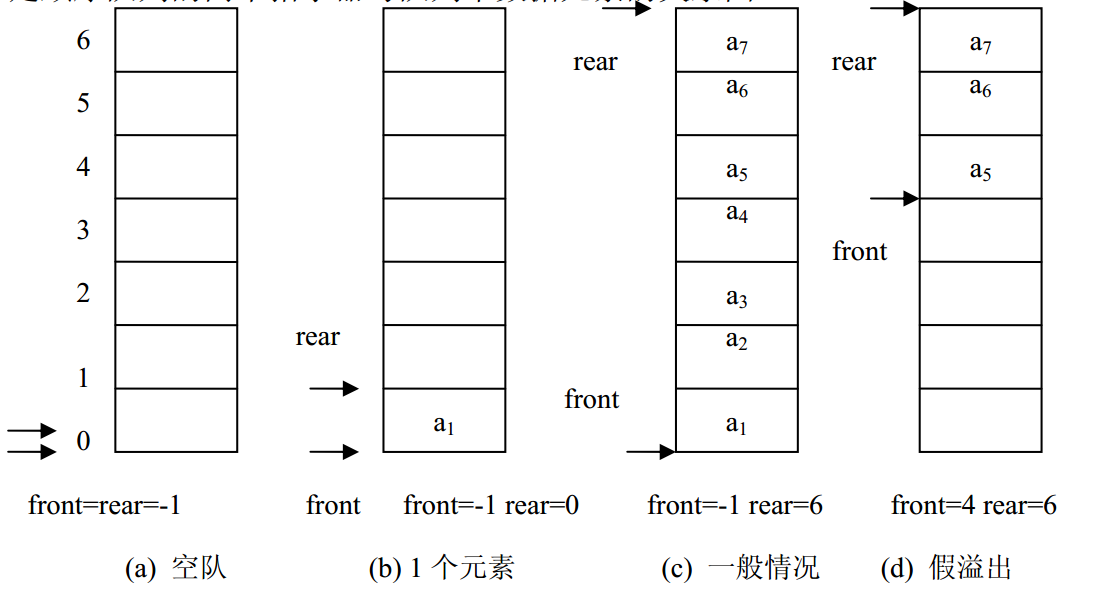
用一维数组来存放顺序队列中的数据元素。队头位置设在数组下标为 0 的端,用 front 表示;队尾位置设在数组的另一端,用 rear 表示。 front 和 rear 随着插入和删除而变化。当队列为空时, front=rear=-1。如下图
创建SeqQueue
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class SeqQueue <T > : IQueue <T > { private T[] data; private int count; private int front; private int rear; public SeqQueue (int size data = new T[size]; count = 0 ; front = -1 ; rear = -1 ; } public SeqQueue () : this (10 } public int Count { get { return count; } } public void Clear () count =0 ; front = rear = -1 ; } public T Dequque () { if (count> 0 ) { T temp=data[front+1 ]; front++; count--; return temp; } else { Console.WriteLine("队列为空,无法取得队首的数据" ); return default (T); } } public void Enqueue (T item ) { if (count == data.Length){ Console.WriteLine("队列已满,不可以再添加新的数据" ); } else { if (rear == data.Length - 1 ) { data[0 ] = item; rear = 0 ; count++; } else { data[rear + 1 ] = item; rear++; count++; } } } public int GetLength () return count; } public bool IsEmpty () return count == 0 ; } public T Peek () T temp = data[front+ 1 ]; return temp; } }
测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Console.WriteLine("************使用代码实现顺序队列************" ); SeqQueue<string > seqQueue = new SeqQueue<string >(); seqQueue.Enqueue("牛魔" ); seqQueue.Enqueue("典韦" ); seqQueue.Enqueue("女娲" ); Console.WriteLine("加入完三个游戏名称后的队列大小为:" + seqQueue.Count); var tempseqQueueOne = seqQueue.Dequque(); Console.WriteLine("取得队首的数据为:" + tempseqQueueOne); Console.WriteLine("出队之后的队列大小为:" + seqQueue.Count); var tempseqQueueTwo = seqQueue.Peek(); Console.WriteLine("取得队首的数据为:" + tempseqQueueTwo); Console.WriteLine("Peek之后的队列大小为:" + seqQueue.Count); seqQueue.Clear(); Console.WriteLine("Clear之后的队列大小为:" + seqQueue.Count); Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------" );
控制台输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ************使用代码实现顺序队列************ 加入完三个游戏名称后的队列大小为:3 取得队首的数据为:牛魔 出队之后的队列大小为:2 取得队首的数据为:典韦 Peek之后的队列大小为:2 Clear之后的队列大小为:0 ---------------------------------------

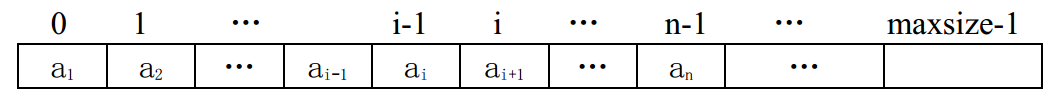
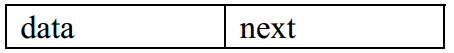









![Unity3d热更新之xLua热更新[基础]](https://cdnimage.gmcj0816.top/img/xlua_cover_one.jpg)
![Unity3d热更新之xLua热更新[C#调用Lua]](https://cdnimage.gmcj0816.top/img/xlua_cover_two.jpg)
